Different Theories That Explain the Formation of Organic Molecules
The occurrence of small organic molecules through unplanned synthesis or since meteorites meeting of these molecules into bigger organic moleculespolymers such as RNA and protein and RNA molecules develop self-replicating the packing of groups of molecules into microspheres that are capable to uphold an interior chemistry dissimilar from surrounds. Their discovery validates models and theories that propose HMT as an important molecule in the formation of organic compounds in interstellar environments.
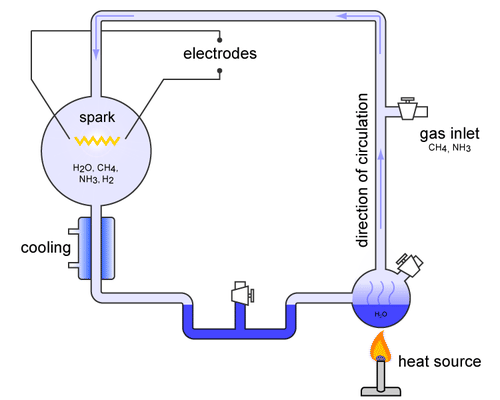
First Organic Molecules Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
Scientists have observed that chemical bonds sometimes form between small organic compounds on hot surfaces.

. Cairns-Smith suggests that mineral crystals in clay could have arranged organic molecules into organized patterns. With two electrons contributed from each 1s orbital of He a total of four electrons would need to be placed into the MOs of HeHe. Organic compounds that can be produced both biotically and abiotically will vary and could include methane or carboxylic acids.
1a the formation of small organic molecules 1b which then combine to form larger biomolecules and 2 the self-organization of these molecules into primitive living organisms. 1 the formation of small organic molecules which then combine to form larger. A Three-Stage Theory Currently conventional theories of chemical-E proposes three major stages.
HMT is a key piece of a puzzle which draws the whole picture of chemical evolution in space said Oba lead author of a paper about the research published December 7 in the journal Nature Communications. Organic compounds are mainly found in most of the living things. The results showthat hydrogenated neutral polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon molecules act as catalysts for the formation of molecular hydrogen.
Wöhlers discovery suggested that life forms like non-living forms were composed of. Benzyne reacts with nucleophilic reagent to form different organic compounds. For origin-of-life researchers here was the possibility that RNA.
This finding helped dispel a theory known as vitalism which taught that living things and their components possessed a vital force At the time scientists believed that living things consisted of organic matter driven by that vital force which separated them from non-living things. First small organic molecules - such as amino acids which make proteins and nucleotides which make DNA - were made. However they were never able to duplicate the conditions themselves.
The magnitude of both cross sections is in line with an EleyRideal type process. Recent hypotheses about the origin of organic molecules suggest that these molecules may have formed in hydrothermal vents deep in the oceans where hot gases and elements emerge from. These compounds are found in non-living things.
The discovery validates theories of the formation of organic compounds in extraterrestrial environments. Just as valence bond theory can explain the formation of the molecule HH it can also explain why the molecule HeHe is not observed. This theory is especially useful to explain the covalent bonds in organic molecules.
The discovery by Thomas Cech that some RNA molecules can catalyze their own site-specific cleavage led to a Nobel prize for Cech and Altman the term ribozymes to denote catalytic RNA molecules and the revival of a hypothesis that RNA molecules were the original hereditary molecules pre-dating DNA. Some scientists hypothesize that some of the first large organic molecules to form and self-replicate were RNA molecules with DNA molecules forming much later. Substitution or displacement reaction.
Organic molecules could have formed spontaneously in Earths early atmosphere and smaller molecules could bond together to build large organic molecules. Their discovery published in the journal Nature Communications validates models and theories that propose HMT as a key molecule in the formation of organic compounds in interstellar environments. In living cells the formation of the large organic macromolecules from smaller organic molecules such as forming proteins from amino acids or forming RNA from nucleotides requires the help of specialized enzymes.
Second these small monomers combined to form larger and more complex. Organic compounds form covalent bonds. The chemistry of life runs on organic compounds molecules.
HD and D2 molecules form through abstraction reactions on deuterated coronene sites with a cross section of 006Å2. Hybridization is a concept used in organic chemistry to explain the chemical bonding in cases where the valence bond theory does not provide satisfactory clarification. This would involve filling both the bonding and antibonding orbitals and any energetic benefit.
The reactions of organic compounds can be classified into four main types. In an attempt to explain how the origin of carbon-based life on earth occurred by abiogenesis a natural non-biological production of life conventional theories of chemical evolution propose two stages in the transformation of lifeless chemicals into life. After a while organic molecules took over this job and organized themselves.
Their experiments indicated that in the primitive Earth atmosphere complex organic molecules could form including amino acids. Inorganic compounds form ionic bonds between the atoms of molecules. In most of the aqueous solutions these are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
The hypothesis they expressed is known as primordial soup. Scientists from Japan and NASA have confirmed the presence in meteorites of a key organic molecule that may have been used to build other organic molecules including some used by life. Previous scientists such as Oparin and Haldane had hypothesized that organic molecules could be created from inorganic molecules that could be found in the atmosphere of the young Earth.

First Organic Molecules Advanced Ck 12 Foundation



Comments
Post a Comment